Companies Rally RISC-V Support for AI and HPC Applications
As RISC-V gains traction as an open-source alternative to Arm, several companies have announced partnerships and research to bolster the ISA.
Forecasts show that AI will continue to fuel RISC-V adoption upward of 50% per year. In response to this demand, several companies have announced partnerships to boost and integrate their RISC-V solutions for AI and high-performance computing (HPC) workloads.
Because it is an open-source ISA, RISC-V has been particularly useful for novel applications for which developers may not have an Arm-based reference to work off. Additionally, RISC-V's small instruction set makes it helpful for energy-efficient designs.
Esperanto and Arteris Partner for RISC-V HPC and AI
In 2022, Esperanto Technologies released its ET-SoC-1 RISC-V processor composed of more than 1,000 energy-efficient 64-bit RISC-V cores. Targeting generative AI and HPC workloads, the ET-SoC-1 reportedly offers up to 50x better performance on key AI workloads. In such large SoCs, there can be hundreds of thousands of control and status registers (CSRs) that allow software to interact with the hardware. These CSRs comprise what is known as the hardware-software interface.

Internal block diagram of the ET-SoC-1 chip. Image used courtesy of Esperanto (See page 35 for enlarged image.)
Esperanto recently selected Arteris’ IP CSRCompiler to manage the complexity associated with the ET-SoC-1's register specification. CSRCompiler, as its name suggests, can take a register specification in a variety of formats—such as an Excel spreadsheet or a specification coded in the proprietary CSRSpec format—and generate RTL, documentation, and verification test benches rapidly. This can drastically reduce development cycle time and time to market, in addition to improving the quality of the RTL since it is also automatically generated.
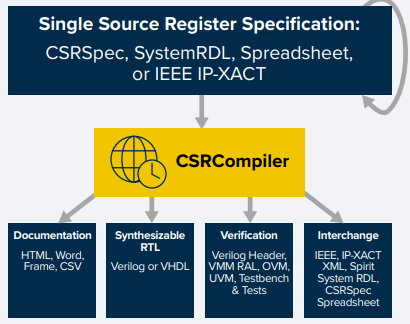
CSRCompiler automatically generates RTL, documentation, and more from register specifications. Image used courtesy of Arteris IP
According to Arteris, CSRCompiler and CSRSpec are easily inserted into an Agile development flow. Agile is a development methodology, traditionally used in software development projects, which has been gaining popularity in hardware to reduce time to market and streamline development. By centralizing and automating the register specification, CSRCompiler allows teams to easily build and maintain the register specification through all steps of the Agile workflow.
Ubuntu Gets a RISC-V Platform
Recently, London-based computer software company Canonical announced an optimized Ubuntu image for the Milk-V Mars platform. The company says it has reached a strategic partnership agreement with Milk-V, with Milk-V providing hardware sponsorship to Canonical for continued improvement of the Ubuntu RISC-V ecosystem.

Milk-V Mars. Image used courtesy of Milk-V
Milk-V Mars is a high-performance RISC-V board about the size of a credit card. It is equipped with 8 GB of RAM and a StarFive JH7110 vision processing platform. It also has various interfaces, including USB, MIPI, and HDMI. With Ubuntu now compatible with the Milk-V Mars, RISC-V enthusiasts and companies can benefit from the huge ecosystem behind Ubuntu. Ubuntu is secure and reliable, in addition to being one of the most popular Linux distributions in the world.
A Lightweight Extension to RISC-V for TNN Inference
With the increasing demand for efficient processing on edge devices like IoT sensors, there's a growing need for AI solutions that minimize energy consumption. Traditional deep neural networks (DNNs) are often too resource-intensive for these platforms. Ternary neural networks (TNNs), on the other hand, are more efficient but have historically required special accelerators to realize this efficiency improvement.
Recently, a group of researchers at ETH Zurich introduced xTern, an extension of the RISC-V ISA for TNNs. XTern enhances throughput by 67% over conventional two-bit methods with only a 5.2% increase in power consumption. This advancement improves energy efficiency by 57.1% and enables up to 1.6 percentage points higher CIFAR-10 classification accuracy on low-power edge AI platforms.

Schematic of the hardware for xTern's threshold-compress. Image used courtesy of ArXiv
xTern improves throughput by optimizing how TNNs are processed on RISC-V processors. By introducing specialized instructions, xTern accelerates the computation of ternary arithmetic operations, leading to faster processing speeds on general-purpose cores. This efficiency boost is essential for enhancing performance in edge AI scenarios while keeping power consumption low.








Professional